Cross-cut test
The cross-cut test is a method for estimating the resistance of a coating to separation from the substrate. For this purpose, sharp cutting edges are used to cut lines with defined spacing through the coating into the substrate in the form of a grid.
Cutting tools with a defined shape of the cutting edges depending on the coating thickness are used for the test. A distinction is made with regard to the cutting devices - single-cutting tools and multiple-cutting tools. A single-cutting tool as well as the multiple-cutting tool are suitable for all types of coatings and substrates. It is important to ensure that all cuts are made on or in the substrate. However, the depth of penetration into the substrate must be as small as possible.
The appearance of the surface can then be assessed visually and the cross-cut values from 0 to 5 given. In some cases, a yes/no assessment is also sufficient. In the case of multi-layer systems, it is additionally indicated between which layers the separation takes place.
Fundamentals
As single-cutting tool with a rigid blade and a V-shaped cutting edge is used. The thickness of the cutting edge is negligible as long as the cutting edge is sharp. A check with regard to the sharpness of the blade is possible by checking the V-shaped cut, which must be uniform over the entire length and thickness of the coating.
Templates are used to ensure a correct cut and the distance between cuts. The loose coating particles are removed.
The GS-Prüfer 6 multi-cutter tool from BYK-Gardner GmbH has a tilting cutting head for optimum alignment on the test surface. The cutting head has six cutting edges with a spacing of 1 mm, 2 mm or 3 mm, as well as a guide edge on the left and right to facilitate handling.
The device used and the type of cutting tool have an influence on the test result and the results cannot be directly compared.
The same cutting tool must be used for each test series. The cross-cut test can be used for coating thicknesses up to 250 µm according to DIN EN ISO 2409.
However, the cross-cut test alone is not suitable for evaluating the adhesion strength of the coatings.
Technical equipment
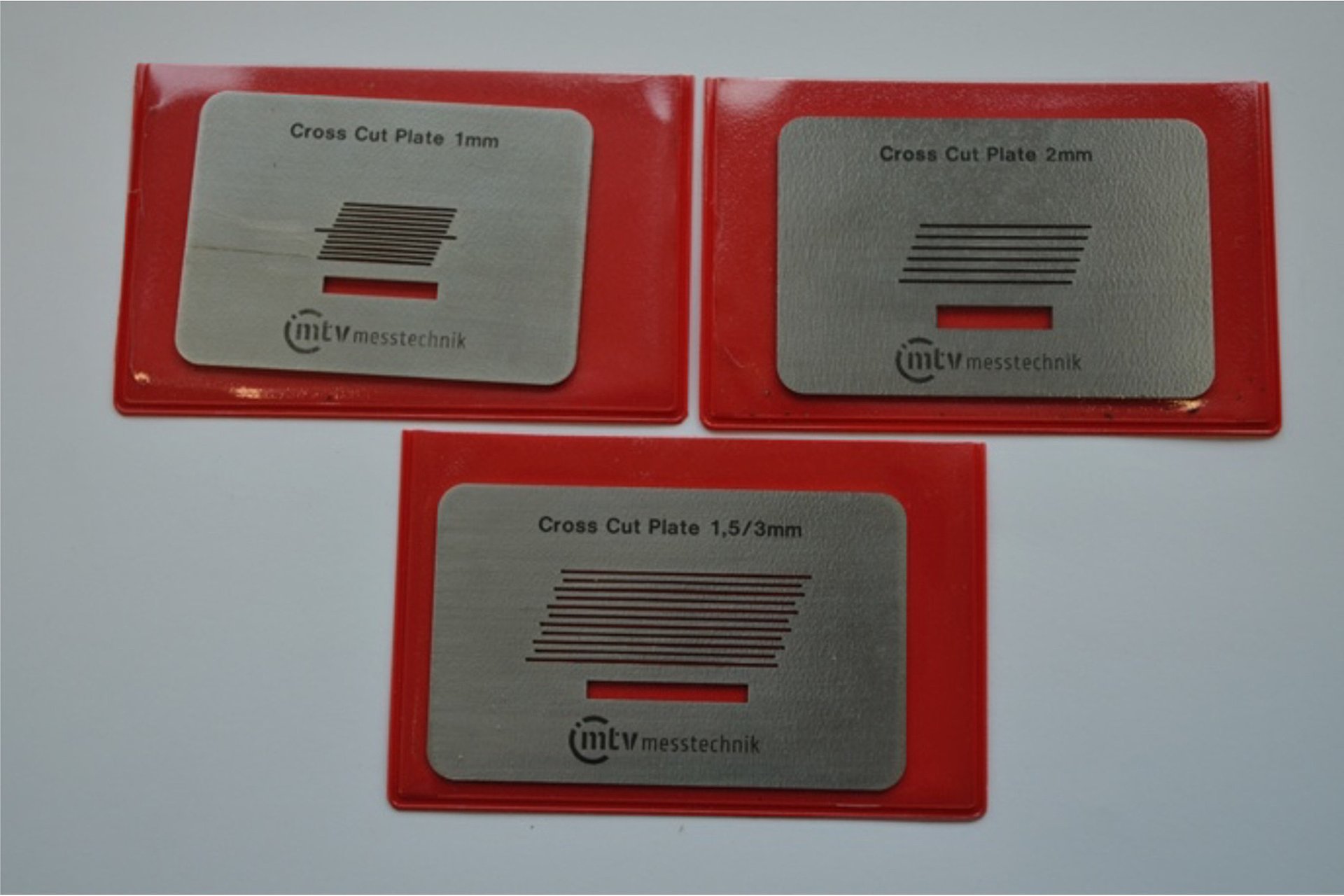

Single-cutting tool
- Cutter with rigid blade and a V-shaped cutting edge
- correct cutting guide and cutting distance with templates
- Cutting distance 1 mm, 1.5 mm, 2 mm and 3 mm
Multi-cutting tool with handle
- Tilting cutting head for optimum alignment on the test surface
- Cutting head with six cutting edges as well as a guide edge on the left and on the right
- Different cutting heads with 1 mm, 2 mm and 3 mm cutting distance
Sample preparation
Preparation
- Test area should be at least 40 mm x 80 mm
- Surfaces must be plane-parallel to the substrate
- Distance from the edges at least 5 mm
Removal of loose particles
- according to DIN EN ISO 2409 three methods possible
- removal with a soft brush
- use of an adhesive tape
- use of compressed air or nitrogen

Test conditions
- Determine the layer thickness to select the appropriate cutting distance.
- Assess whether the substrate is soft or hard
- Layer thickness up to 60 µm - 1 mm cutting distance for hard substrates
- Layer thickness up to 60 µm - 2 mm cutting distance for soft substrates
- Layer thickness up to 61 µm up to 120 µm - 2 mm cutting distance for hard and soft substrates
- Layer thickness up to 121 µm up to 250 µm - 3 mm cutting distance for hard and soft substrates
Standards
Akkreditierte Normen
- DIN EN ISO 2409:
Beschichtungsstoffe – Gitterschnittprüfung
Weitere Normen
- ISO 16276-2:
Korrosionsschutz von Stahlbauten durch Beschichtungssysteme – Beurteilung der Adhäsion/Kohäsion (Haftfestigkeit) einer Beschichtung und Kriterien für deren Annahme – Teil 2: Gitterschnitt- und Kreuzschnittprüfung
Results
- Cross-cut values 0 to 5
- Yes / No statement
Dr.-Ing. Marcus Schoßig
Phone: +49 (0)3461 30889-53
Write e-mail
